INDUSTRY ESSENTIALS
Preventing mother-to-child transmission of HBV: Local recommendations on antenatal screening and management
The 2024 guidelines developed by the Hong Kong College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (HKCOG) respond to the pressing public health challenge of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, which affects approximately 296 million people worldwide and is responsible for around 820,000 deaths each year, primarily from cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.1
A key focus of these guidelines is the elimination of mother-to-child transmission (MTCT) of HBV, which aligns with the World Health Organization's goal to reduce the prevalence of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) in children under 5 to ≤0.1% by 2030.1 Evidence indicates that timely administration of the HBV vaccine and hepatitis B immunoglobulin (HBIG) can significantly decrease MTCT rates.1 Furthermore, including women with lower viral loads in treatment protocols has been shown to improve outcomes for both mothers and infants.1
The guidelines offer a comprehensive framework for the individualized care of pregnant women with HBV.1 They emphasize the importance of monitoring viral load, gestational age, and the mode of delivery to optimize health outcomes.1 This tailored approach ensures that all HBV-infected pregnant women receive appropriate screening, treatment, and monitoring throughout their pregnancy.1 By enhancing maternal and infant health through effective prevention of MTCT, clinicians are empowered to play a vital role in achieving the WHO's goal of eliminating viral hepatitis as a public health threat, in alignment with the objectives of the Hong Kong Viral Hepatitis Action Plan 2020-2024.1
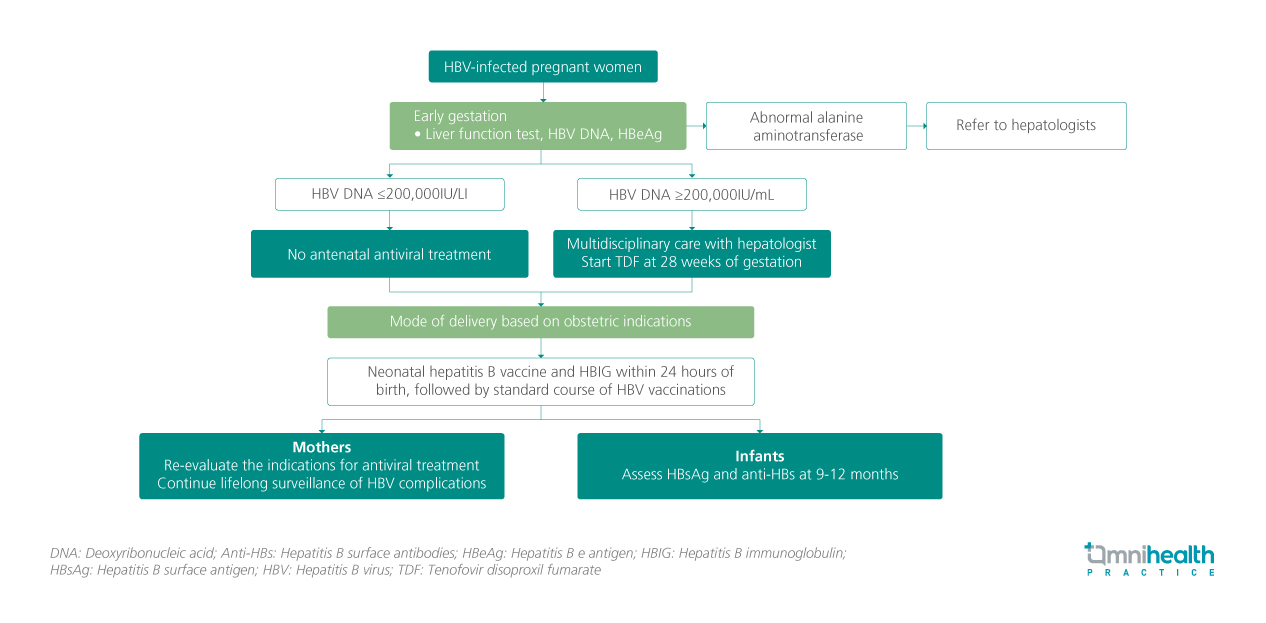
Recommendations of the HKCOG for the prevention and management of HBV infection
|
Prevention of mother-to-child HBV transmission |
|
1. All pregnant women should undergo HBsAg screening in early pregnancy |
|
2. All infants should receive the birth dose of hepatitis B vaccine as soon as possible (within 24 hours after delivery), followed by the 2nd and 3rd doses at 1 month and 6 months of age, respectively |
|
3. Infants born to HBV-infected mothers should receive the birth dose of HBIG when they receive the birth dose of hepatitis B vaccine |
|
Use of antenatal antiviral treatment to prevent IF |
|
4. HBV-infected pregnant women should undergo assessments of HBV DNA level, HBeAg status, and baseline liver function in early pregnancy to determine the need for antiviral prophylaxis to prevent MTCT of HBV and the need for antiviral treatment to manage maternal indications |
|
5. There is no need for repeat HBV DNA quantification in later stages of pregnancy. HBV DNA levels typically remain stable during pregnancy and similar cut-offs could be used to predict the risk of IF |
|
6. For women with an HBV DNA level of >5.3 log10IU/mL (>200,000IU/mL), multidisciplinary care involving hepatologists is advised to discuss the indications and safety of antenatal TDF to reduce the risk of IF |
|
7. For women with an HBV DNA level of ≤5.3 log10IU/mL (≤200,000IU/mL), reminders should be established for long-term regular monitoring and follow-up after delivery, in accordance with established protocols for patients with chronic HBV infection |
|
Continuation of antiviral treatment after delivery |
|
8. Multidisciplinary care is essential to ensure that women are counseled about the existing evidence and allowed to engage in thorough discussions with the treating physician regarding the risks and benefits of the timing for cessation of prophylactic treatment |
|
9. Importantly, although most flares are mild and spontaneously resolved, liver function tests should be performed every 3 months for 6 months after cessation of prophylactic antiviral treatment |
|
10. HBV-infected pregnant women receiving antiviral treatment for maternal indications should continue therapy, even after delivery, and be managed in accordance with standard protocols |
HBIG: Hepatitis B immunoglobulin; HBeAg: Hepatitis B e antigen; HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; IF: Immunoprophylaxis failure; MTCT: Mother-to-child Transmission; TDF: Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate
Recommended pathway for managing HBV-infected women during pregnancy and after delivery