CONFERENCE UPDATE: EASD 2023
Combined antiviral treatment of pleconaril and ribavirin decelerates the development of newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes in adolescent populations: Results from the DiViD Intervention study
STUDY DESIGN
The association between enterovirus infections and the onset of type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1D) was evident as the results of a recently published meta-analysis suggested that patients with T1D were 16 times more likely to experience enterovirus infections when compared to healthy controls.1 In addition, pancreatic tissue samples collected from 6 patients with recent T1D onset in the Diabetes Virus Detection (DiViD) study indicated a low-grade enterovirus infection and antiviral response across all cases.1 As such, a few speculations emerged regarding the potential link between enteroviruses and the progression of T1D.
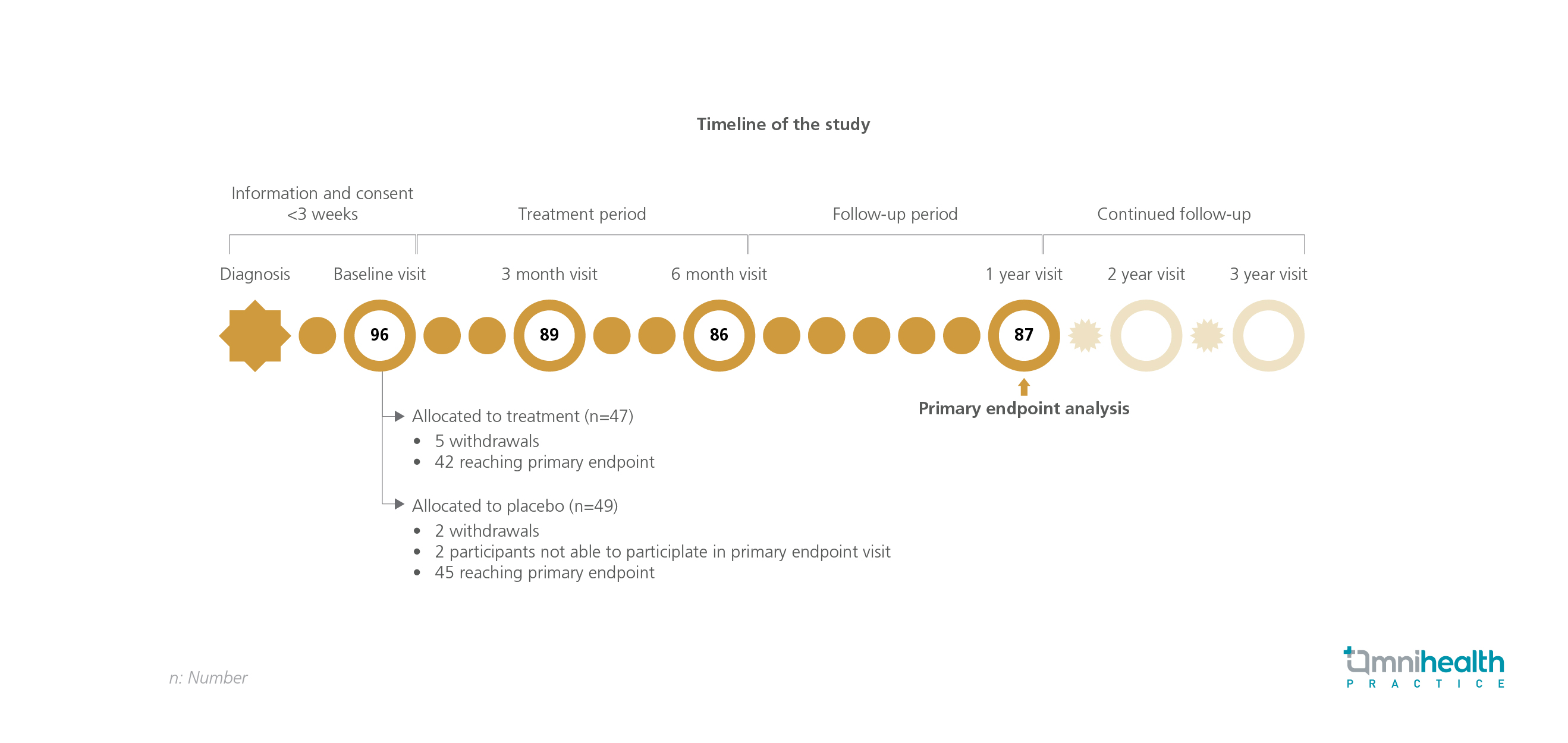
The DiViD Intervention study was a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, clinical trial conducted to assess the effect of antiviral treatment on beta cell function in children and adolescents with recent onset of T1D.1 A total of 96 patients aged 6 to 16 years with T1D who received their first insulin injection within 3 weeks prior to study inclusion were randomized to receive oral solutions of pleconaril (10mg/kg/day) and ribavirin (15mg/kg/day) (n=47) or placebo (n=49) twice daily for 26 weeks.1
The primary endpoint of this study was the endogenous insulin production at 12 months, measured by the 2h C-peptide area under the curve (AUC) during a mixed meal tolerance test (MMTT).1 Secondary endpoints included safety, the proportion of patients with a peak C-peptide of >0.2pmol/ml, as well as changes in HbA1c and glycated albumin levels from the baseline.1
| Primary endpoints: |
|
|
| Secondary endpoint: |
|
|
|
|
|
| Safety: |
|
|
|
“These results strengthen the possible link between enteroviruses and the development of T1D and provide a rationale for further evaluating antiviral strategies in the treatment of newly diagnosed T1D and prevention of prediabetes progression”
Dr. Ida Maria Mynarek
Oslo University Hospital,
Oslo, Norway

