INDUSTRY ESSENTIALS
Local consensus on CKD management: Integrating global standards for localized care
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) has a significant global impact, affecting over 800 million people, particularly those from lower socio-economic backgrounds.1 In Hong Kong, recent survey data indicate that 0.7% of individuals aged 15 and older have been diagnosed with renal impairment.1 CKD is classified into five stages, with stages 4 and 5 linked to considerably higher risks of mortality and cardiovascular complications.1 Early detection and intervention are crucial for preventing the progression to kidney failure and for effective risk stratification, especially since over 40% of individuals with diabetes—a major risk factor for CKD—are likely to develop the condition.1
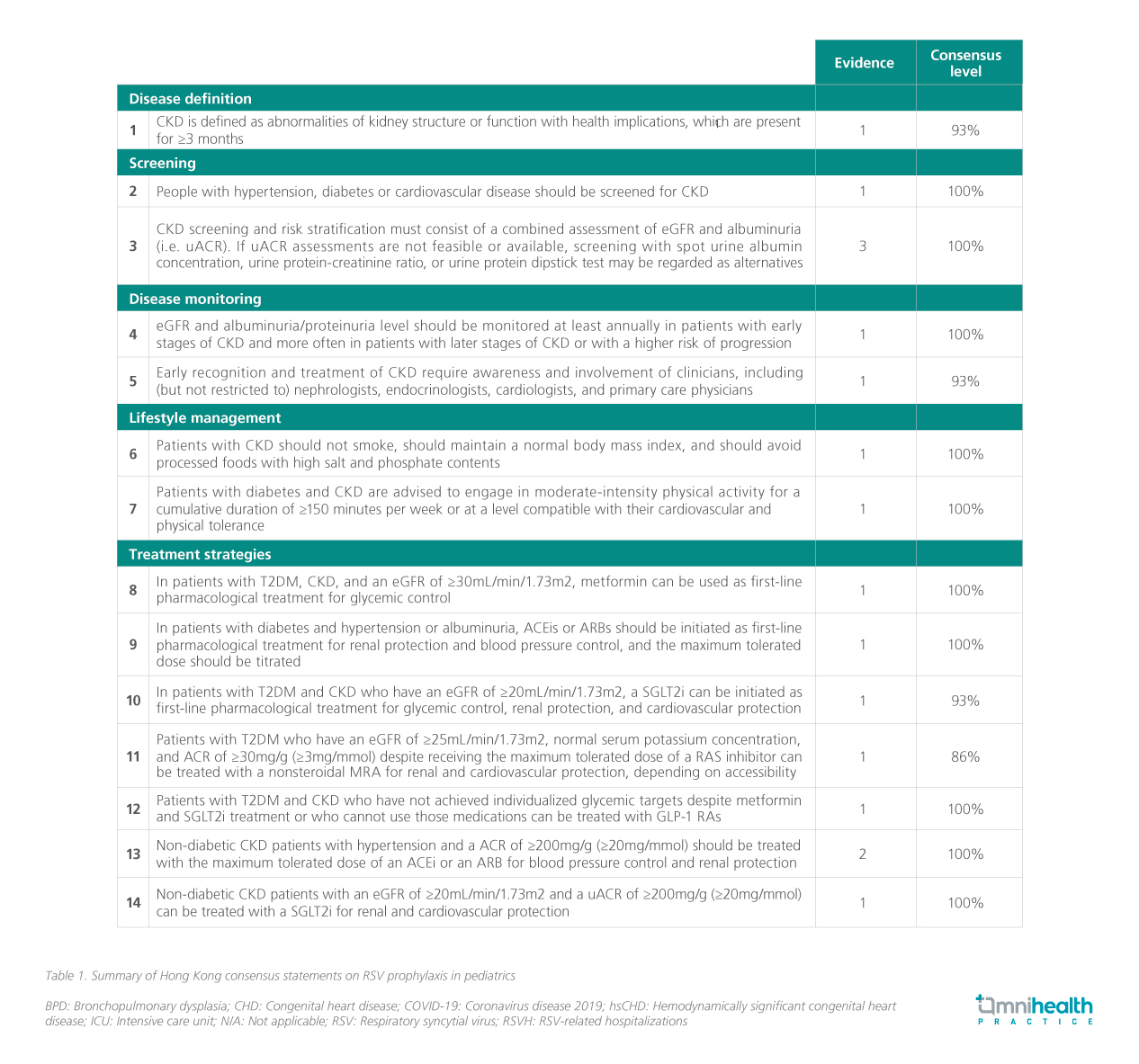
Despite the critical need for early identification and management of CKD, Hong Kong has yet to establish a consensus on best practices, and existing guidelines have not been widely adopted due to inadequate incentives.1 To address this gap, the Management of CKD: A Hong Kong Consensus Recommendation was developed, offering practical guidance for local healthcare practitioners grounded in evidence and expert opinion.1 An expert panel, including nephrologists, endocrinologists, and family medicine specialists, formulated these recommendations using a modified Delphi process.1
The panel reviewed peer-reviewed literature on CKD published between January 2017 and September 2022, encompassing clinical trials, guidelines, and systematic reviews, to draft initial statements on the definition, screening, and management of CKD.1 Each draft statement was evaluated using a 5-point Likert scale: A (fully accept), B (accept with minor reservations), C (accept with major reservations), D (reject with reservations), and E (fully reject).1 Statements were revised as needed, followed by a second round of voting.1 A consensus was achieved when at least 75% of panel members either fully accepted the statement or accepted it with reservations.1 Ultimately, 14 statements met this consensus threshold (table 1).1