CONFERENCE UPDATE: APLAR 2022
Update on COVID-19 infection and vaccination management in SLE
The prevalence of Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patient is higher than in the normal population and SLE patients being associated with higher risk of death from COVID-19.1 The COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel (hereinafter referred to as “The Panel”) from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) COVID-19 Vaccine Clinical Guidance Task Force updated their COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines and Guidance for Management of Rheumatic Disease in Adult Patients During the COVID-19 Pandemic (i.e., version 5) in 2022.1 At the 24th Asia-Pacific League of Associations for Rheumatology (APLAR) conference held in December 2022, Dr. Laniyati Hamijoyo from the University of Padjadjaran, Indonesia, highlighted the updates on the management of COVID-19 infection in SLE patients and COVID-19 vaccination for SLE.1
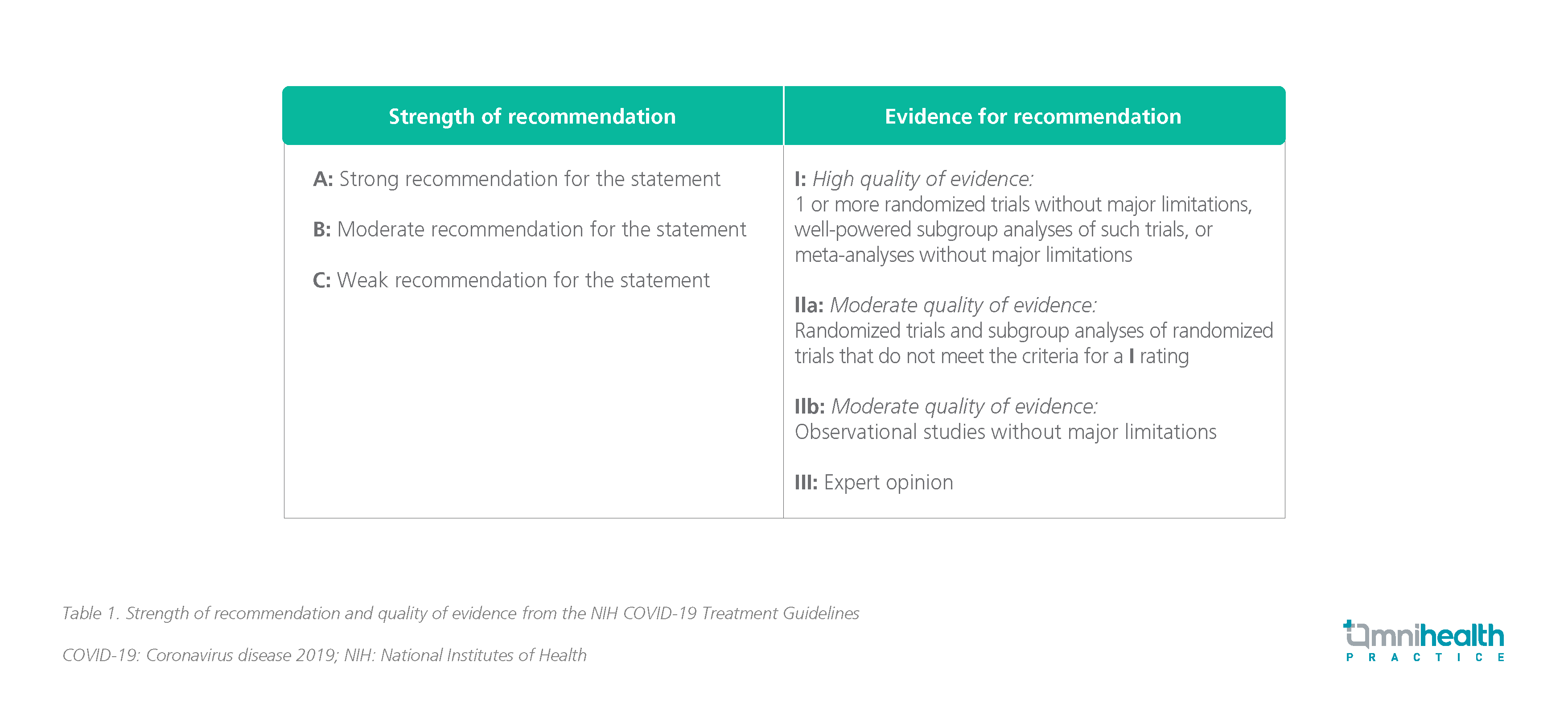
With respect to the NIH guidelines for treating COVID-19, the strength of recommendation and the quality of evidence are as follows:
The management of COVID-19 infection in SLE patients
- The following are selected recommendations for special consideration in people who are immunocompromised:
- Pre-exposure prophylaxis is recommended to treat this group of patients prior to exposure
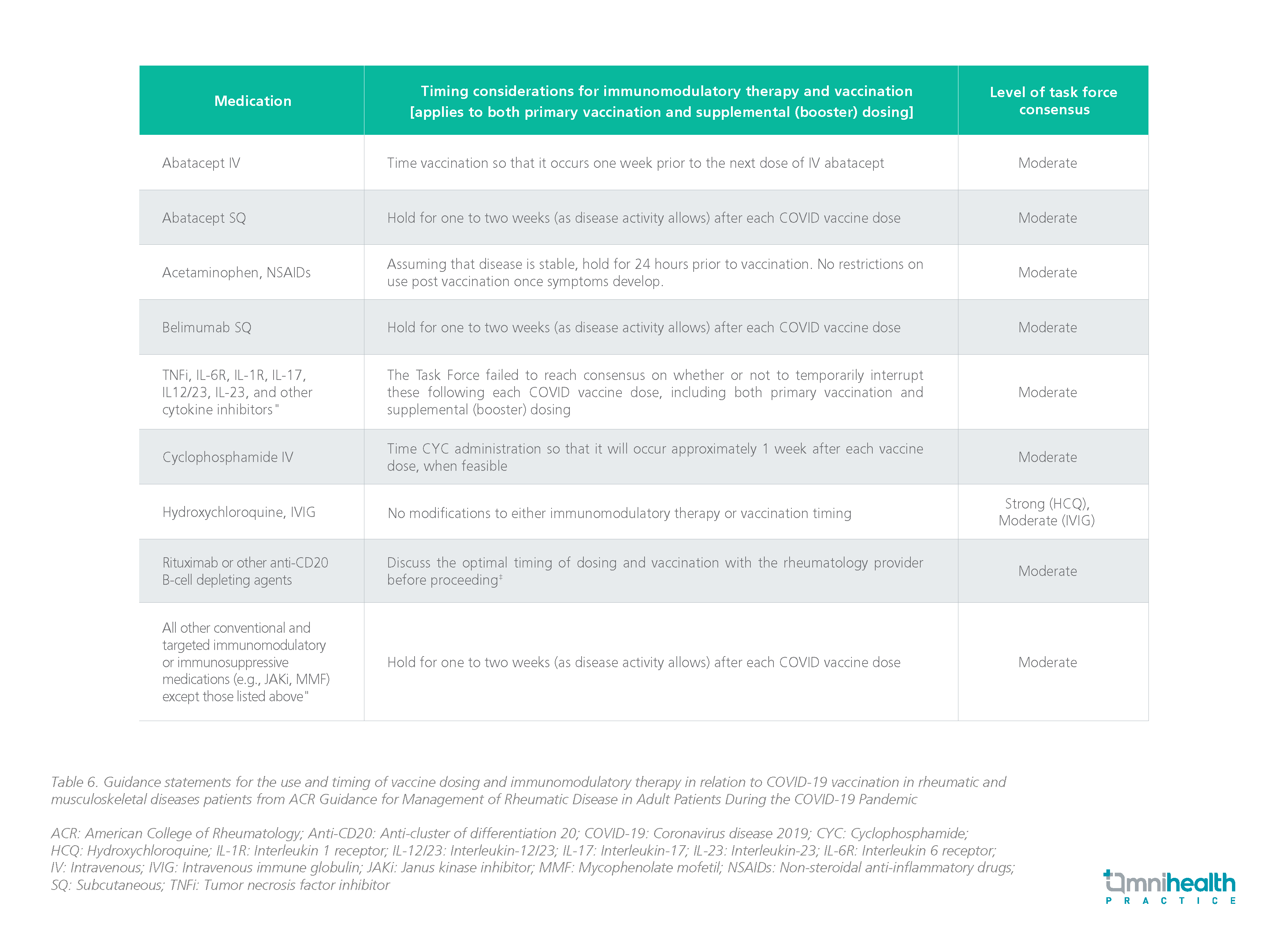
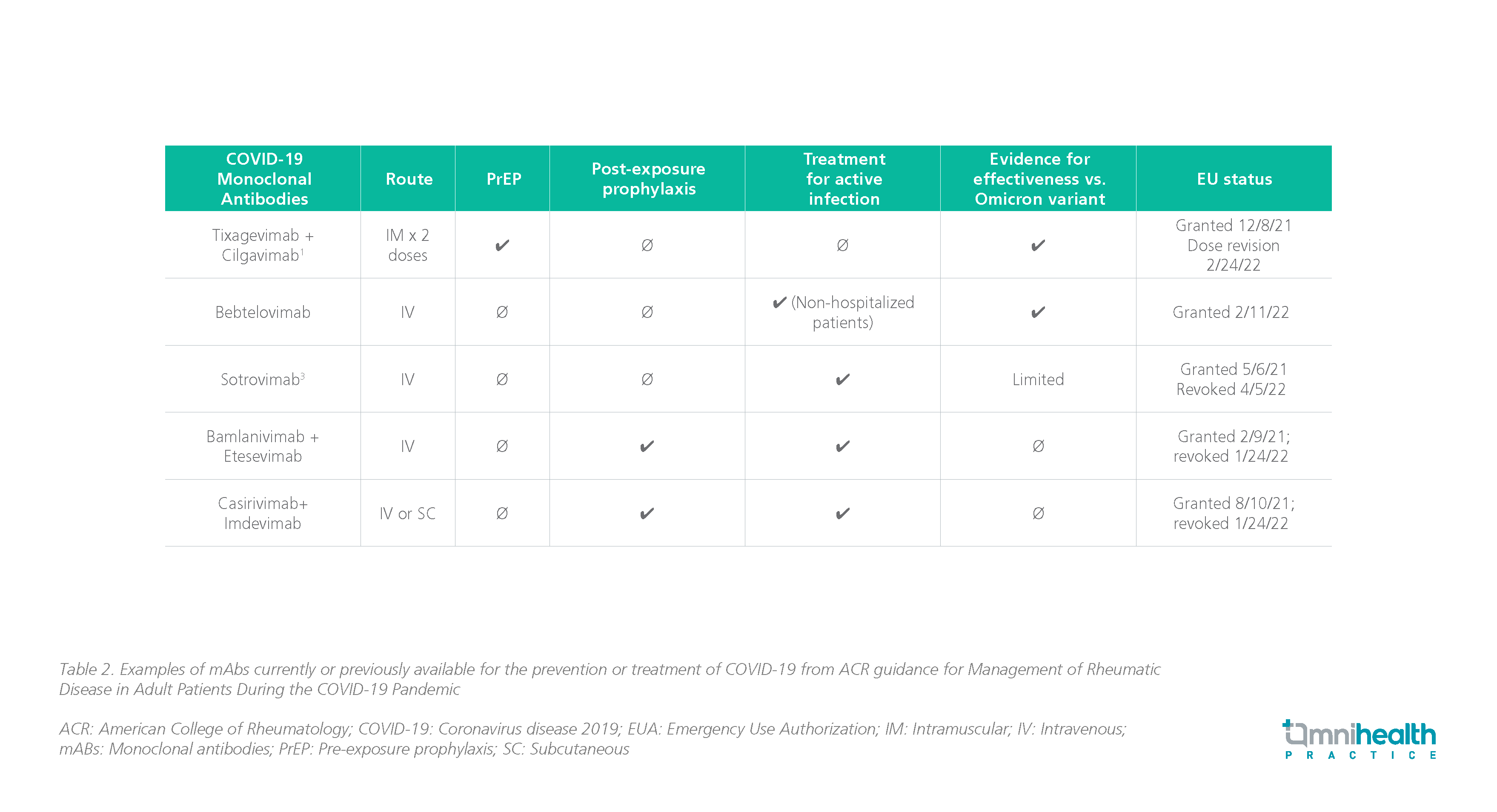
- Anti-severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus type 2 (SARS-CoV-2) monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) tixagevimab (300mg) + cilgavimab (300mg) is recommended as intramuscular (IM) injections for adults and adolescents who do not have SARS-CoV-2 infection or recent exposure to an individual with SARS-CoV-2 infection and who are moderately to severely immunocompromised and may have an inadequate immune response to COVID-19 vaccination (BIIb)
- For the general management of COVID-19 patients who are immunocompromised:
- Decision regarding stopping or reducing the doses of immunosuppressive drugs in COVID-19 patients be made in consultation with the appropriate specialists; Clinicians should consider factors such as the underlying disease, the specific immunosuppressants being used, the potential for drug-drug interactions (DDIs), and the severity of COVID-19 (BIII)
- Decision regarding stopping or reducing the doses of immunosuppressive drugs in COVID-19 patients be made in consultation with the appropriate specialists; Clinicians should consider factors such as the underlying disease, the specific immunosuppressants being used, the potential for drug-drug interactions (DDIs), and the severity of COVID-19 (BIII)
- For therapeutic management of non-hospitalized COVID-19 patients who are immunocompromised:
- Prompt treatment with antiviral or anti-SARS-CoV-2 mAbs is recommended for non-hospitalized patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 who are immunocompromised (AIII)
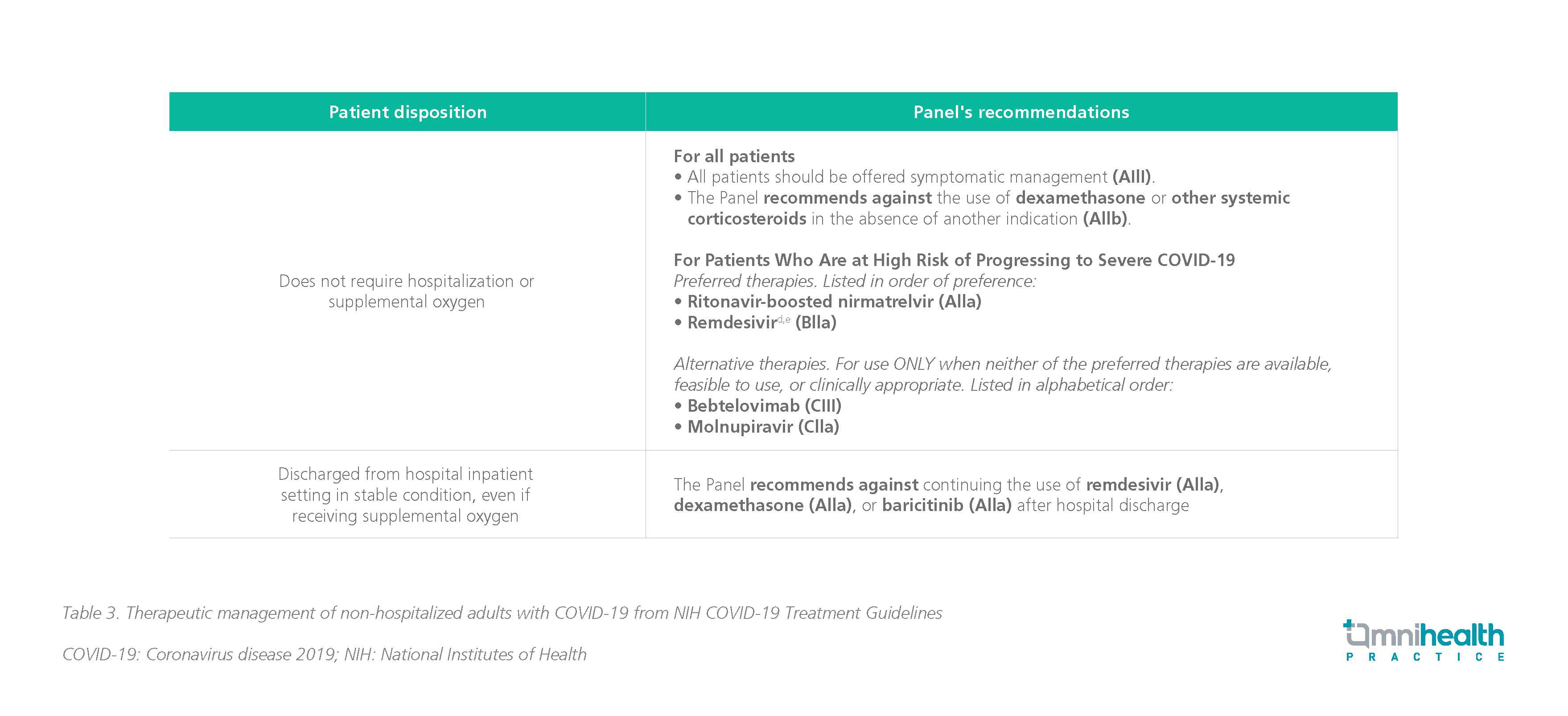
- For therapeutic management of hospitalized COVID-19 patients who are immunocompromised:
- Patients with COVID-19 who are immunocompromised and were hospitalized for illnesses other than COVID-19 should get the same treatment as patients who were not hospitalized (AIII).
- The Panel advises administering immunomodulatory treatments and antiviral medications in most immunocompromised COVID-19 patients at the dosages and durations advised for the general population (AIII).
- Immunomodulatory medication regimens may need to be modified in some circumstances to limit the risk of DDIs, overlapping toxicities, and secondary infections.
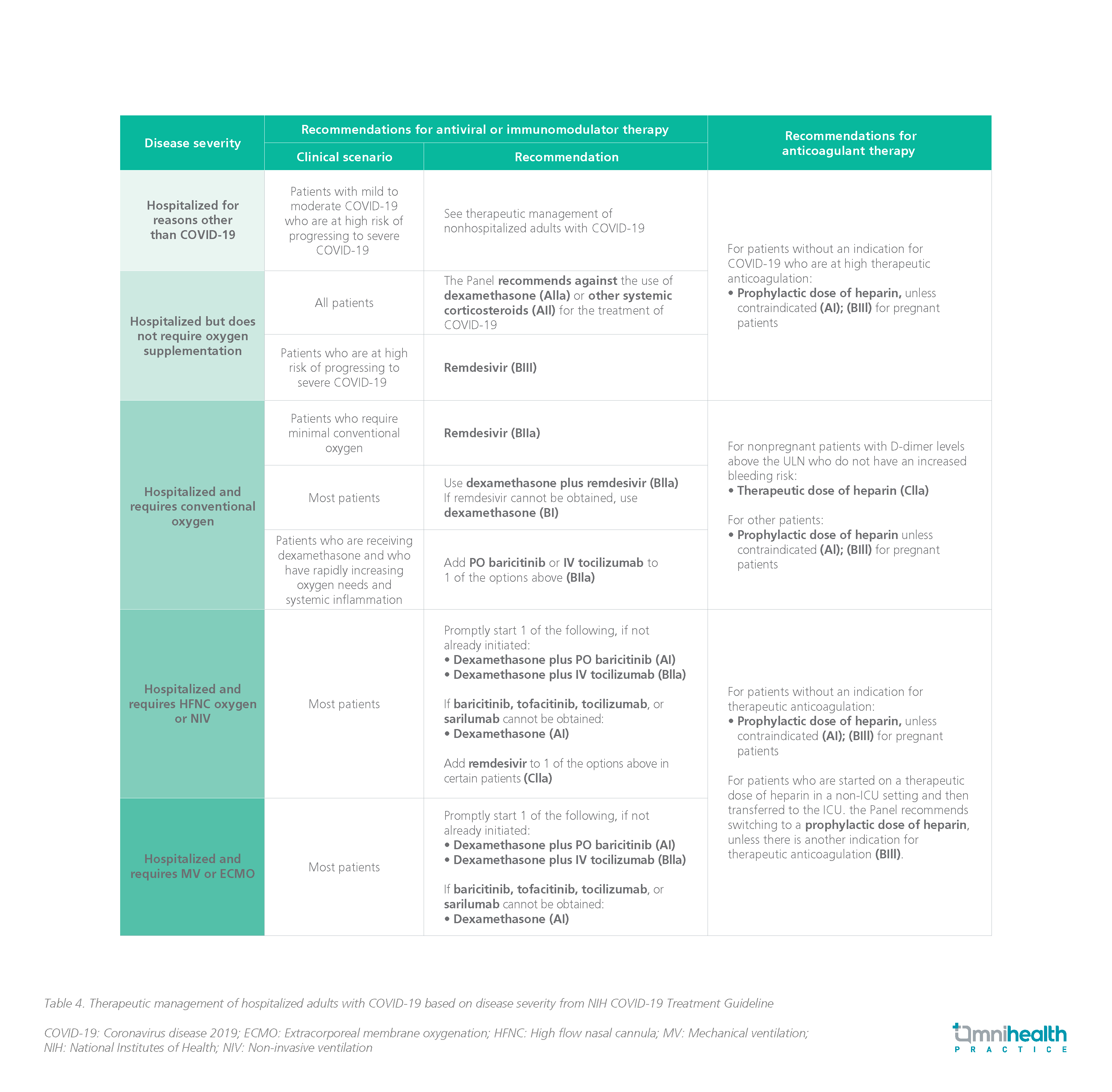
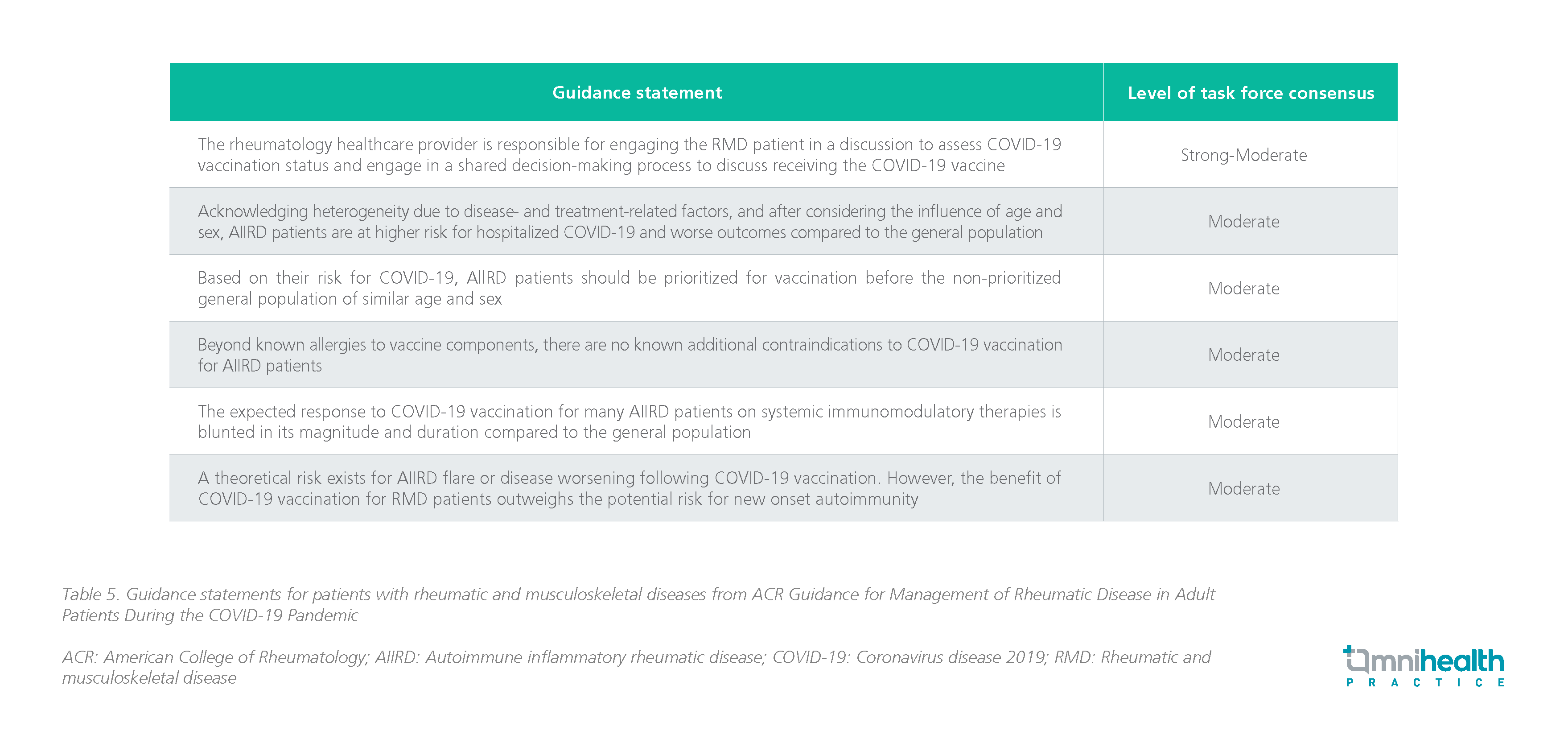
COVID-19 vaccination for SLE patients
- The following are selected recommendations for special consideration in people who are immunocompromised:
- The Panel recommends COVID-19 vaccination for all people who are moderately or severely immunocompromised (AIII).
- All close contact of people who are immunocompromised are strongly encouraged to be up-to-date on vaccination against COVID-19 (AIII).
- Vaccinating household members, close contacts, and healthcare workers who provide care for patients who are immunocompromised is important to protecting patients from infection.