CONFERENCE UPDATE: AAN 2025
Tolebrutinib slows disability progression in nrSPMS: Results from the phase 3 HERCULES trial
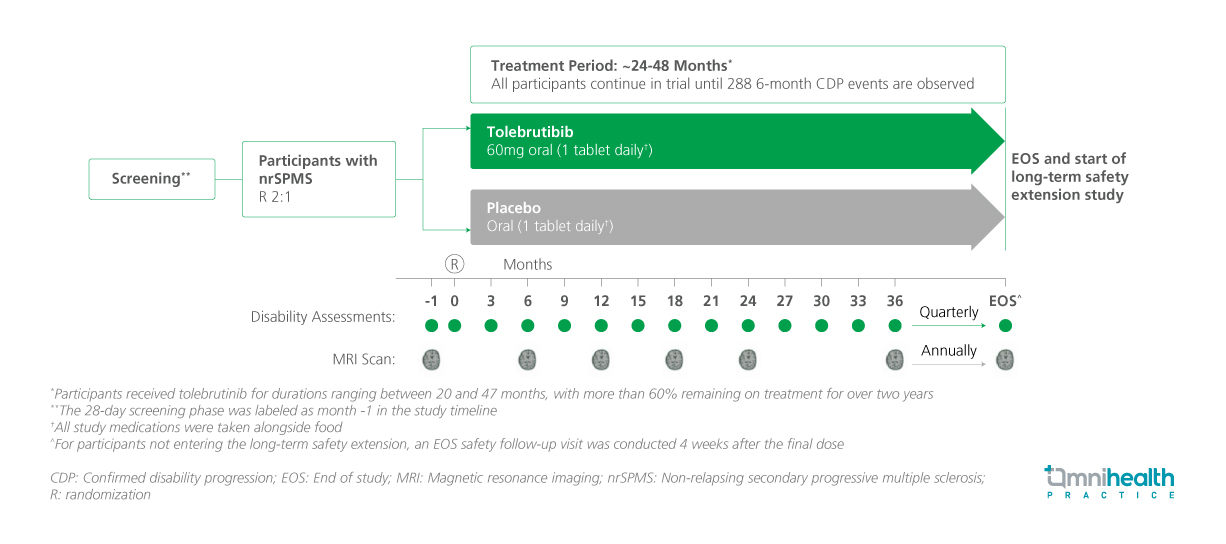
STUDY DESIGN
In multiple sclerosis (MS), disability accumulation often begins early in the disease course and is believed to result from chronic, smoldering neuroinflammation.1 The HERCULES trial was a phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, event-driven study designed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of tolebrutinib, a central nervous system-penetrant Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor, in delaying disability progression in patients with non-relapsing secondary progressive multiple sclerosis (nrSPMS).1
In the HERCULES trial, a total of 1,131 patients were randomized 2:1 to receive tolebrutinib 60mg orally once daily (n=754) or placebo (n=377).1 Eligible participants were aged 18-60 years, had an expanded disability status scale (EDSS) score of 3.0-6.5, had no clinical relapses within the prior 24 months, and demonstrated confirmed disability progression within the previous year.1 Baseline demographic and clinical baseline characteristics were similar and well-balanced between the two treatment arms.1
The primary endpoint of the study was the time to onset of 6-month confirmed disability progression (CDP), which was defined as an increase of ≥1.0 points from baseline in the EDSS score for participants with a baseline score of ≤5.0, or an increase of ≥0.5 points for those with a baseline score >5.0.1 Key secondary endpoints included the time to onset of 3-month CDP, time to onset of a sustained 20% increase in performance time on the 9-Hole Peg Test (9-HPT) for at least three months, and time to onset of a sustained 20% increase in the Timed 25-Foot Walk (T25-FW) over the same duration.1 Other secondary endpoints included the time to onset of 6-month confirmed disability improvement (CDI), defined as a decrease of ≥1.0 point from baseline in the EDSS score, confirmed over six months, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) outcomes, such as the total number of new or enlarging T2 lesions and the percentage change in brain volume.1
FINDINGS
|
Primary endpoint: |
|
|
Secondary endpoints: |
|
|
Safety: |
|

