CONFERENCE UPDATE: EADV 2024
The impact of secukinumab on mental well-being in patients with moderate to severe HS: Post-hoc analysis of the SUNSHINE/SUNRISE trials
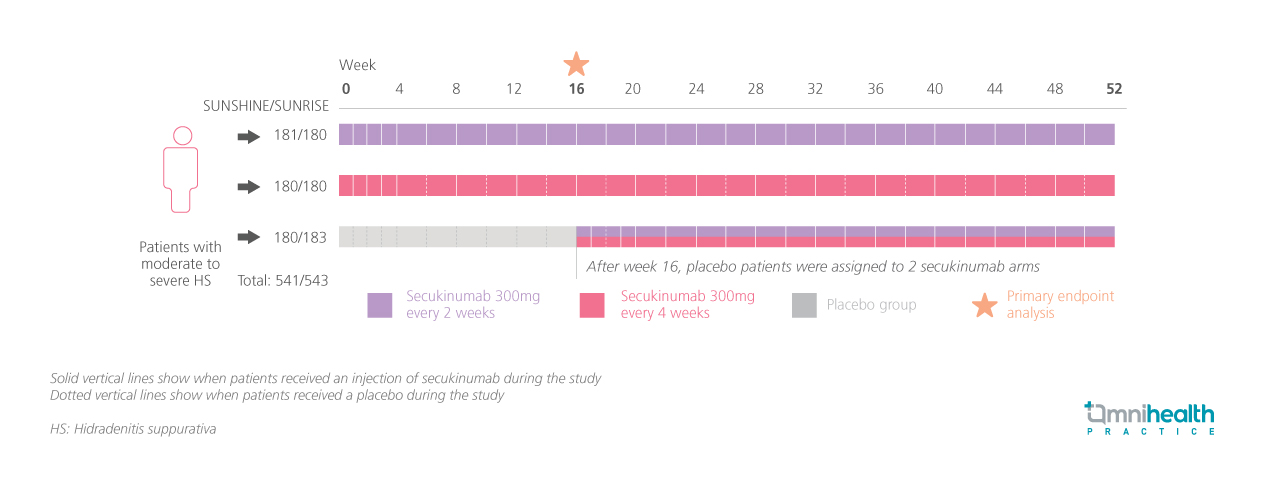
STUDY DESIGN
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that significantly impacts patients' quality of life (QoL).1 Individuals with HS often experience comorbidities, including psychiatric conditions such as depression and anxiety, with recent findings indicating they are about twice as likely to develop these disorders compared to those without HS.1 Secukinumab has shown sustained efficacy in moderate to severe HS in the SUNSHINE and SUNRISE phase 3 trials, improving QoL while maintaining a favorable safety profile over one year.1
The post-hoc analysis of pooled data from these trials assessed psychiatric comorbidities at baseline and through week 52 in patients treated with secukinumab.1 In both trials, patients were randomized to receive subcutaneous secukinumab 300mg every 2 weeks (SECQ2W) or 4 weeks (SECQ4W), or placebo for 16 weeks.1 After this period, placebo patients switched to secukinumab while those on SECQ2W and SECQ4W continued their treatment until week 52.1 A total of 1,084 patients were enrolled, with a mean age of 36.2 years and 56.3% being female.1
The analysis assessed the frequency of psychiatric comorbidities at baseline, focusing on reports of "psychiatric disorder," "depression," and "anxiety," along with the concomitant use of medications for these conditions during the trial.1
The impact of secukinumab on psychiatric symptoms was assessed using 2 patient-reported outcome measures.1 Mood was evaluated through the "anxiety/depression" item of the European QoL 5-Dimension (EQ-5D) questionnaire up to week 52.1 Emotional impact was measured using the HS Symptom and Impact Diary (HSSID), where patients rated the negative impact of HS on their emotions over the past 24 hours on a 0-3 scale.1 Incidence of new or worsening psychiatric adverse events was also reported through week 52.1 All analyses were exploratory with no statistical
"These findings highlight the positive benefits achieved by patients when treated with secukinumab for HS, particularly with respect to mental and emotional well-being, which is likely due to a holistic effect and overall symptom improvement in patients with HS"
Professor Jacek Szepietowski Department of Dermatology,
Venereology and Allergology,
Wroclaw Medical University, Wroclaw, Poland
FINDINGS
| Psychiatric comorbidity profile: |
|
|
|
|
|
| EQ-5D outcomes: |
|
|
| HSSID outcomes: |
|
|
| Safety: |
|
|
|

