CONFERENCE UPDATE: EULAR 2024
Impact of ixekizumab on structural lesions in SIJ of patients with r-axSpA: Post-hoc analysis of the COAST-V trial
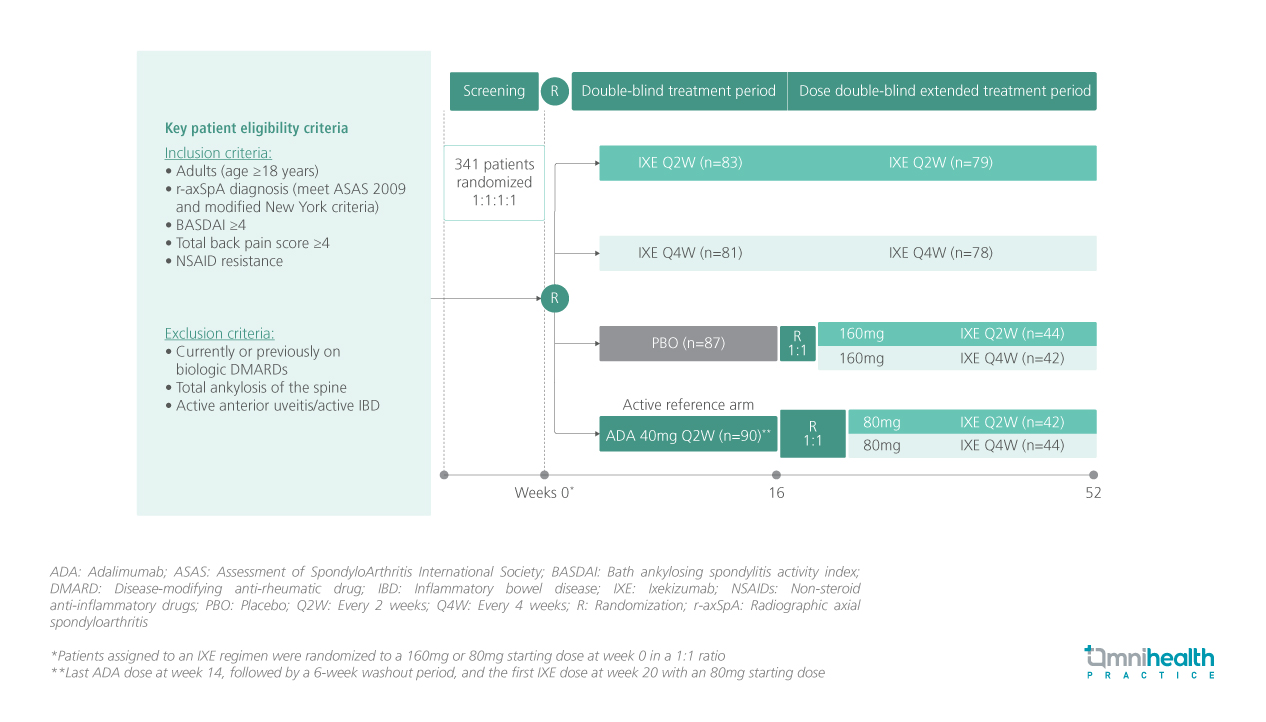
STUDY DESIGN
Ixekizumab (IXE) is a monoclonal antibody that selectively inhibits interleukin (IL)-17A, which plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (r-axSpA).1 Previously, IXE has been demonstrated to improve signs and symptoms of r-axSpA, but the effect of IXE on structural lesions in the sacroiliac joints (SIJ) of r-axSpA patients remains unknown.1
COAST-V is a 52-week phase 3, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo (PBO)-controlled and active-controlled trial involving bio-naïve adult patients with active r-axSpA (n=341).1 They were randomized 1:1:1:1 to receive PBO, 80mg subcutaneous IXE every 2 weeks (Q2W), IXE every 4 weeks (Q4W), or 40mg adalimumab (ADA) Q2W as an active reference.1 In week 16, patients in the PBO and ADA groups were randomized 1:1 again to receive IXE Q2W or Q4W.1
This post-hoc analysis evaluated the effect of IXE on structural lesions in SIJ at baseline, week 16, and week 52.1 The effect of IXE was evaluated by changes in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) structural lesions as assessed using the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC) sacroiliac joint structural scores (SSS) for 4 lesion types including erosion, backfill, fat metaplasia, and ankylosis.1 After adjusting for baseline SPARCC values, baseline SPARCC bone marrow edema (BME) and stratification factors, covariance analysis was conducted to compare treatments based on observed data for each type of lesion.1 Sensitivity analyses were adjusted for different baseline factors and subsets of patients with less severe ankylosis scores.1 Changes in structural lesions were stratified by sex, HLA-B27 status, and SPARCC BME baseline cutoffs of ≥4 and <4 for subgroup analyses.1
FINDINGS
| Efficacy outcomes: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Subgroup analyses: |
|
|
|
|

