CONFERENCE UPDATE: EHA 2025
Gilteritinib continues to improve OS in R/R FLT3-mutated AML at 3-year follow-up of the Asian-centric phase 3 COMMODORE trial
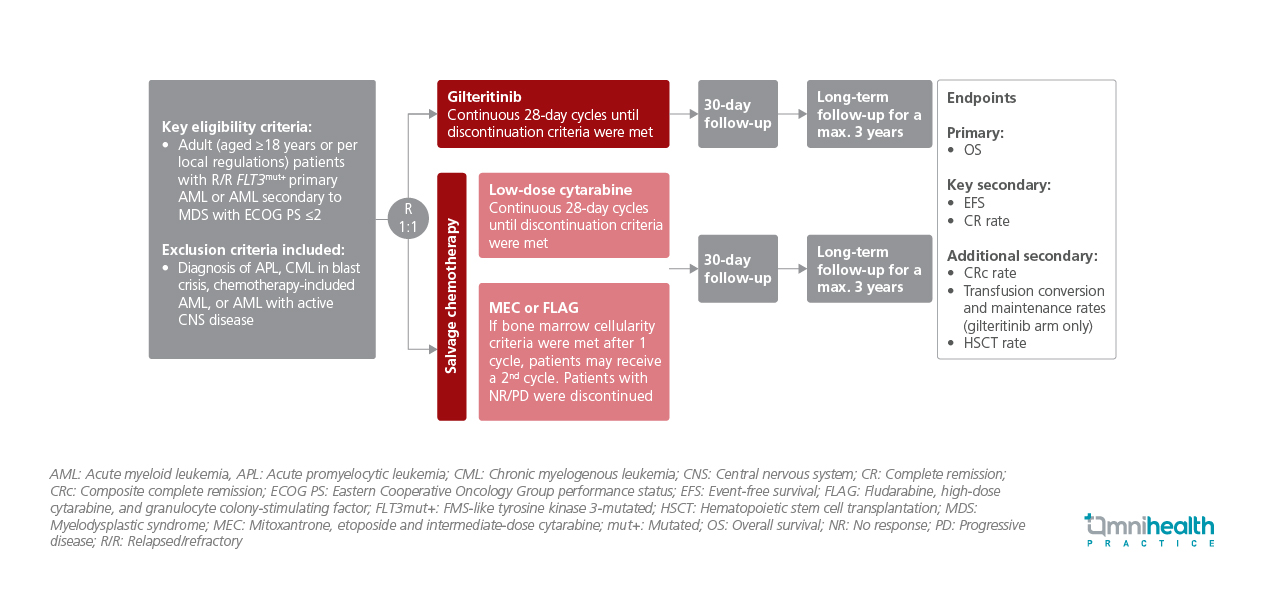
STUDY DESIGN
Relapsed or refractory (R/R) FLT3-mutated acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is associated with a poor prognosis.1 While global trials have demonstrated that gilteritinib offers superior survival benefits and a favorable safety profile compared to standard chemotherapy, long-term randomized data in Asian populations remain limited.1 The COMMODORE study aimed to address this evidence gap by evaluating the long-term efficacy and safety of gilteritinib in a predominantly Asian cohort with R/R FLT3-mutated AML.1 In the primary analysis with a median follow-up of 10.3 months, gilteritinib significantly improved overall survival (OS) and event-free survival (EFS).1 This presentation described the long-term (3-year) follow-up results from the COMMODORE study in predominantly Asian patients.1
The COMMODORE study was a phase 3, randomized, open-label, multicenter trial conducted across 48 clinical sites in China, Malaysia, Thailand, Singapore, and Russia.1 Adults (≥18 years) with confirmed FLT3-mutated AML, either de novo or secondary to myelodysplastic syndrome, and an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status ≤2 were randomized 1:1 to receive either oral gilteritinib (120mg/day) (n=137) or investigator-selected salvage chemotherapy (n=139).1 Patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia, blast-phase chronic myeloid leukemia, active central nervous system (CNS) disease, or chemotherapy-induced AML were excluded.1 Baseline characteristics were balanced between arms, and the majority of patients were Asian.1
The primary endpoint was OS.1 Secondary endpoints included event-free survival (EFS), complete remission (CR) rate, composite complete remission (CRc) rate, overall response rate (ORR), hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) rate, transfusion conversion rate, and maintenance rate (for the gilteritinib arm only).1
FINDINGS
|
Primary endpoint: |
|
|
Secondary endpoints: |
|
|
Safety: |
|

